Lecturer:
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Huỳnh Công Pháp
Material
Part 1. Fundamentals and principles of networking programming
History and fathers of the Internet | Packet switching vision | Network visualization
History, big picture, layering
Tier 1, 2, 3 ISPs | Transcontinental cable layout | Gateway between cellular and Internet- Layering (end to end horizontal communication) and inspiration from airline system
Internet terminology, nuts and bolts
- Devices, end-hosts, routers, switches, links, applications, protocols, connection less/oriented services- Network edge and network core, Client server, P2P, hybrid, edge-fog-cloud- Network access and media: Notion of FFT and bandwidth, dial-up, ADSL, cable …
Foundations: SNR, Bit rate, Bit error, Shannon’s equation, Congestion
- Circuit switching [FDM, TDM], Packet switching [Datagram, Virtual vircuit], statistical multiplexing
Internet protocol stack, layering, encapsulation
- Foundations: Throughput, goodput, latency (queueing, processing, transmit time, propagation delay)- Traffic arrival and service rate, properties of queueing delay, end-to-end delay, Traceeroute
Protocol Stack: ISO OSI Model – 07 layers
Understand functionalities and how data is transmitted and processed via each layer of OSI Stack.
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol. TCP/IP Stack is specifically designed as a model to offer highly reliable and end-to-end byte stream over an unreliable internetwork.
Introduction and basics
- Client server, pure P2P, and hybrid architectures; Overlay networks, social networks.- Leader election, flooding, broadcast storm, (adaptive) gossip, index servers, hash tables- Process, sockets, service requirements (data loss, bandwidth, latency)
- Web and HTTP: protocol, request response messages, persistent and non persistent, cookies- Cookies, Web caching and dbenefits, conditional GET, Email (SMTP, MAP), POP, IMAP
- DNS, root, TLD, authoritative servers, recursive and iterative, P2P networks [napster, Gnutella, Kaaza]
Introduction and definitions
- End to end transport, definition of reliability, bottleneck bandwidth, connection orientation service- Packet-pair based bottleneck estimation
Principles of reliable protocol design
- Reliable service over an unreliable channel, Error detection and correction- impossibility of distributed concensus (2 generals), state machines- Building basic reliablity protocol with channel models [bit error, packet loss, packet delay]
From correctness to Performance
- Channel error model: packet delay –> larger sequence number space- Pipelined protocols: Go back N
Pipelined protocols
- Continue on Go Back N (GBN)- Selective ACK (SACK) or Selective Repeat, True/False conditions on Tx and Rx window
TCP:
From principles to the real world
- Bottleneck and available bandwidth, adapting congestion window (CW)- Connection set up, slow start (double CW every RTT), congestion avoidance (CW + 1 every RTT)
The core TCP protocol
- Packet drops and timeout, benefit of cumulative ACK, DupACKs and implications on congestion- Fast Recovery (3 DupACKs): need for CW to increase despite in congestion avoidance
The protocol state diagram
- Fast recovery continued, TCP state diagram (full protocol)- Saw tooth behavior, single timer, RTO estimation
Wrapping up TCP
- RTO estimation, packets to bytes, TCP Flow control- TCP fairness, TCP RED (random early drop) and cross layer ideas, TCP over wireless (split TCP and SNOOP)
Introduction
- Introduction, routing and forwarding, connection set up, network service models- Virtual circuit and datagram networks, forwarding table
Routers and IP
- Longest prefix matching algorithm, Router architecture, Switching fabric, input/output interfaces- IP network protocol, datagram format, fragmentation, Subnet masks, Classless address
Modules in IP
- Classless addressing (CIDR), route aggregation, NAT, ICMP- Traceroute as ICMP, Hourglass model, IPv6 and tunneling, Routing algorithms (graphs)
Routing algorithms
- Link state routing: Dijkstra’s algorithm, convergence, oscillation, complexity- Distance vector routing: Bellman-Ford’s algorithm, convergence, poisson reverse
Internet routing protocols
- Hierarchical routing protocols, autonomous system (AS)- Intra and inter-AS routing protocols, RIP, OSPF, hierarchical OSPF
Inter-AS routing protocol
- Border gateway protocol (BGP)- Hot potato routing and socio-political aspects of routing
Introduction
- Introduction to link layer; local reliability as optimization (not correctness)
Foundation
- End to end reliability versus link-layer reliability, error detection and correction codes (parity)- Noise (additive Gaussian), SNR and SINR, packet collision- Medium access control (MAC), point-to-point and shared link, centralized versus distributed protocol
Medium Access Control
- Channel partitioning (TDMA, FDMA), Random Access (ALOHA and unslotted ALOHA) – Carrier sense multiple access (CSMA), collision detection, exponential backoff, contention window – Taking turns (polling, token passing)
Addressing and Interconnects
- Review of CSMA/CD, flowchart, important properties of protocol, Ethernet case study – MAC adddresses, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) – Hubs and Switches, collision domains, plug and play, cut-through switching, comparison with routers
- Wireless channels: dispersive, collision detection breaks, SINR is key – Hidden and exposed terminal problem, 2 conditions to satisfy for collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) – WiFi protocol (RTS/CTS/Data/ACK), problems with channel reservation, error contrast in wired and wireless
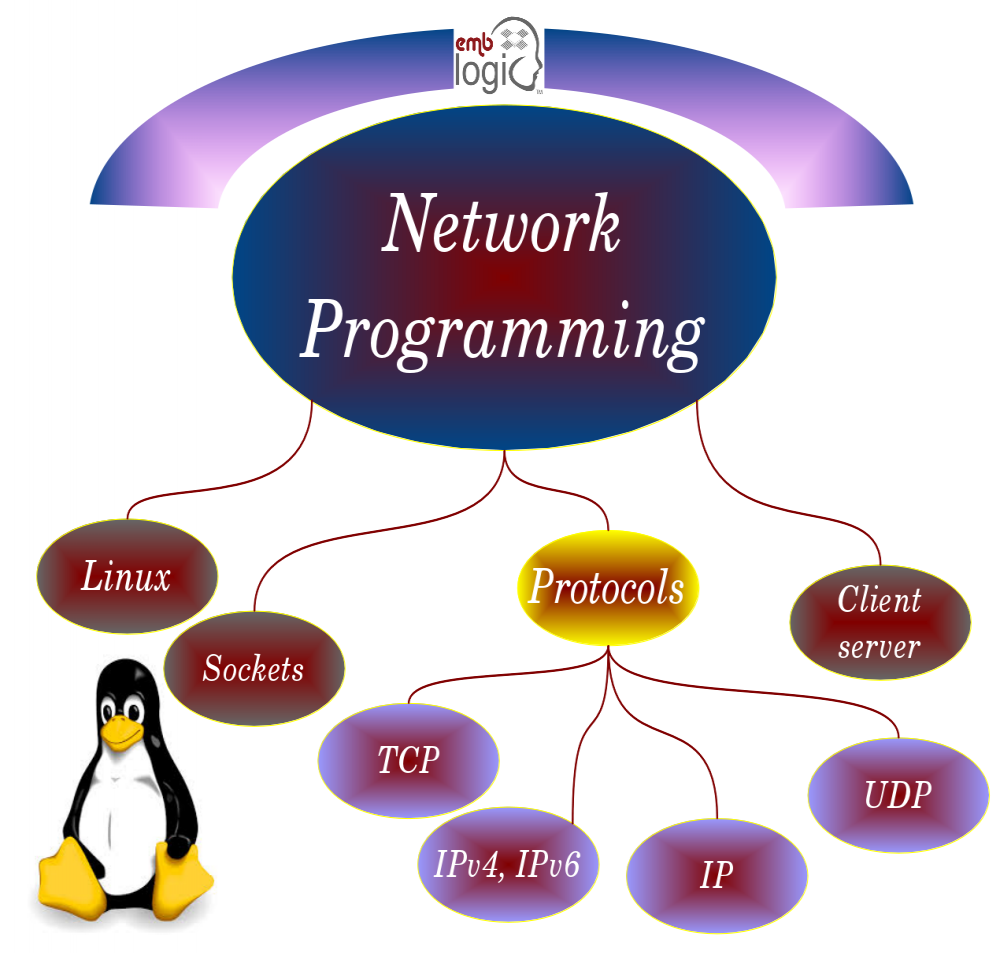
Part 2. Implementation of network applications
![]() Multiserver and distributed programming
Multiserver and distributed programming
Part 3. Security in network programming
Security foundations: Confidentiality, authentication, integrity, availability- Ciphers, cryptography (symmetric and public-key), RSA algorithm, properties of public and private keys- Authentication, nonce, replay attack, man in the middle attack, spoofing- Message integrity, digital signature, hashing, SHA-1 and MD5.
Key distribution center (KDC), Certification authority (CA)- Secure email as an application offers confidentiality, integrity, authentication, efficiency- Course wrap up: final exam logistics, quick Internet bird’s eye view, follow-up courses, feedback.
Basics
- Security foundations: Confidentiality, authentication, integrity, availability – Ciphers, cryptography (symmetric and public-key), RSA algorithm, properties of public and private keys – Authentication, nonce, replay attack, man in the middle attack, spoofing – Message integrity, digital signature, hashing, SHA-1 and MD5
Wrap Up
- Key distribution center (KDC), Certification authority (CA) – Secure email as an application offers confidentiality, integrity, authentication, efficiency – Course wrap up: final exam logistics, quick Internet bird’s eye view, follow-up courses, feedback.
